Consider reviewing the basics with the following content:
- Getting Started with Python: Project 0 – “Hello, World”
- Getting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide pt3
- Getting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide (pt 2)
- Getting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide (pt 1)
Terminal Window – Command Line Interface
This tutorial uses Visual Studio Code:
To create and edit a Python file, use the command line in the integrated terminal. For example:
code Hello.py
This command opens a new file named Hello.py in your code editor. Inside Hello.py, write:

This is one of the most famous first programs in programming.
Python
Python is a programming language and an interpreter that translates your code into machine language (0s and 1s) that the computer can understand. This is the mission of Python.
Understanding Functions and Arguments
To understand this process, we need to understand functions. A function is an action or verb that the computer or language knows how to perform.
These functions are what we use to have the computer perform actions we desire. In the example above, print is a function.
A function can take arguments—the input to the function that influences its behavior. The print function has parentheses where we can add arguments, determining what we want to print on the screen.
For example:

Here, "Hello, world" is the argument for the print function. The result is that “Hello, world” gets printed on the screen. This is known as a side effect.
Handling Errors
If there’s an error in your code, it creates a bug—a mistake that you need to resolve. This is where time and practice come in, as you work on resolving mysterious bugs in a program.
For example, consider this code:

This code will raise a SyntaxError because it is missing a closing parenthesis ). These bugs can get more complicated, but understanding and resolving them is a crucial part of programming.
Summary
- Terminal Window: Used to execute commands.
- Python: A language and interpreter for writing and running code.
- Functions: Actions or verbs that the language can perform.
- Arguments: Inputs to functions that influence their behavior.
- Errors: Bugs or mistakes in the code that need to be resolved.
By practicing and troubleshooting these concepts, you can become proficient in programming and debugging your code.
Making the Program More Interactive
Let’s get more complex and make the program more interactive for the user.
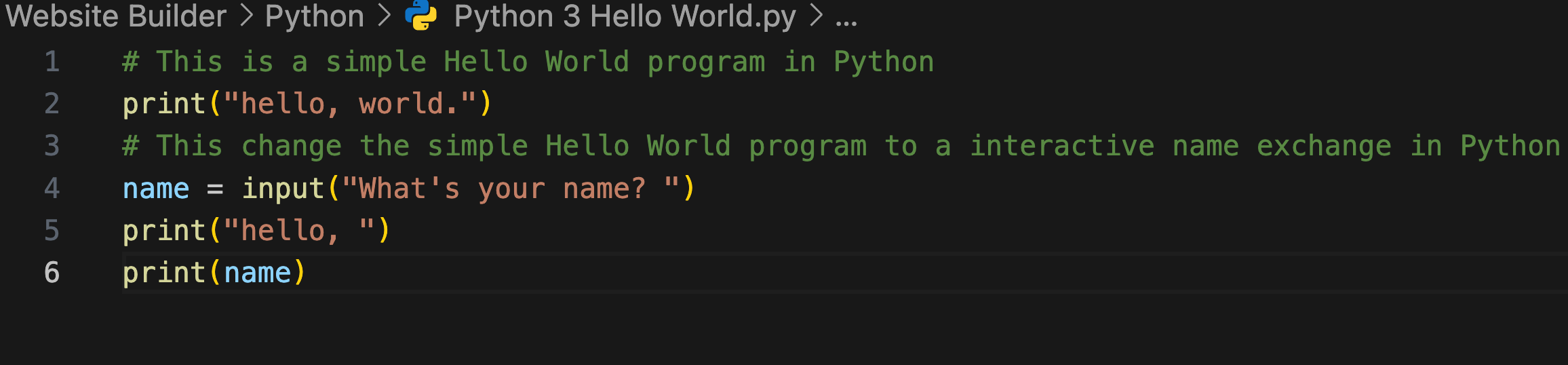
To make this more interactive, we can ask the user for their name and then greet them personally. Here’s how we can do it:
- Printing to the User
- We start by asking the user for their name:

- Better: Getting Input from the User
- Instead of just printing a message, we can use the
inputfunction, which waits for the user to enter a response.
- Instead of just printing a message, we can use the

The input function displays a prompt (in this case, “What’s your name? “) and waits for the user to type something and press Enter. The user’s input is then stored in the variable name.
But we want to have a call-and-response style. This is where the Return Function is important. We then need a variable, which is a container of value.

In this code:
name = input("What's your name? ")– This line assigns the user’s input to the variablename.print(name)– This line prints the value of thenamevariable.
We are going to stop here but I hope this was fun for you. Please dont forget to subscribe!
Check out this source for advanced learning.
https://cs50.harvard.edu/python/2022/weeks/0/: Getting Started with Python: Project 0 – “Hello, World”Also, if you’re not a big fan of subscribing but want to show thanks, you can totally just donate whatever custom amount you have in mind for the work. Your support is much appreciated for me to get more content out for you! 😄
Make a one-time donation
Make a monthly donation
Make a yearly donation
Choose an amount
Or enter a custom amount
Your contribution is appreciated.
Your contribution is appreciated.
Your contribution is appreciated.
DonateDonate monthlyDonate yearlyGetting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide pt3
In the first two parts of our beginner’s guide to Python, we covered variables, data types, conditional statements, collections, loops, and functions. In this final part, we will delve into…
Getting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide (pt 2)
n the second part of our Python beginner’s guide, we delve into collections like lists, tuples, and dictionaries, and explore control flow mechanisms such as loops and functions. Enhance your…
Getting Started with Python: A Beginner’s Guide (pt 1)
This guide covers the basics of Python, including variables, data types, operators, and conditional statements. It explains the concepts with examples and provides a foundational understanding for programming in Python.



Leave a comment